7. TC UNIT FUNCTIONALITY
The operation of the unit is as below:
Diagram B shows the unit in the "cold" condition.
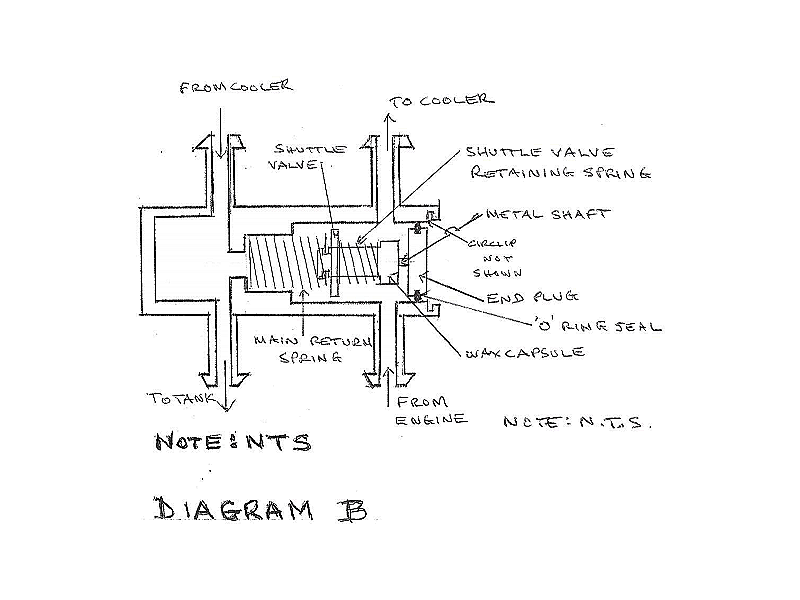
Oil flows from the engine into the thermostat where it surrounds the wax capsule. The oil then has two possible routes to follow.
Firstly it can go straight on and to the cooler. Secondly it can go past the wax capsule, around the outside of the shuttle valve, through the coils of the main return spring and through the connection back to the oil tank.
With the oil cold the oil cooler resistance is very significant and the second route described means that the cold oil effectively "by-passes" the cooler and provides a low resistance path for the oil.
When the oil is cold the vast majority of the oil by-passes the cooler and is returned to the oil tank without going through the cooler and therefore without being cooled.
As the temperature of the oil increases to the control temperature of the wax capsule the wax starts to change phase and the metal shaft of the wax capsule is forced out of the wax capsule. As the outer end of the shaft butts against the end cap this end cannot move and so the wax capsule is forced into the body housing against the force from the main return spring.
As the temperature continues to increase the capsule and valve move to the position shown in Diagram C.
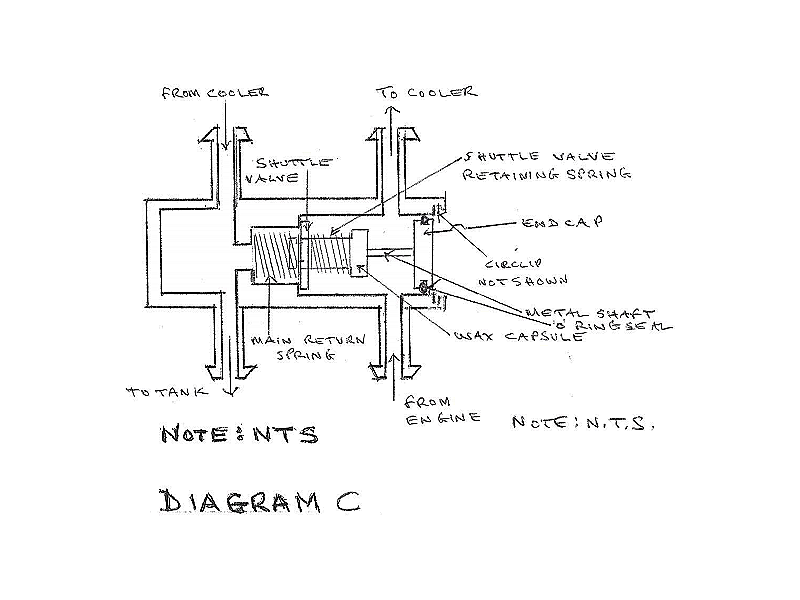
Here the shuttle valve has moved so that it presses against the step in the body housing and effectively blocks the oil flow in the by-pass mode. This is not a 100% seal - but probably not far off it. This means that virtually 100% of the oil flow then passes to the cooler and the cooled oil then returns to the oil tank.
This is not a precision instrument so further movement of the metal shaft out of the wax capsule past the point where the shuttle valve seats on the body housing step means that the wax capsule moves through the shuttle valve thereby further compressing the shuttle valve return spring.
As the oil temperature from the engine cools down or the engine is stopped and the oil temperature reduces then the process reverses back to the "cold" condition.